Impact of Radio Equipment Directive (RED) on IoT Security and the way forward
The EU Radio Equipment Directive (RED) – especially the 2021 Delegated Regulation on cybersecurity – significantly reshapes IoT development by making cybersecurity and privacy compliance mandatory. These rules, enforceable from August 2025, affect all connected devices marketed in the EU, demanding changes across hardware design, firmware, data handling, and conformity assessment.
📌 1. What is RED and What’s Changing?
🎯 Core Objective of RED (2014/53/EU):
Originally aimed to ensure safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and efficient spectrum use for radio equipment sold in the EU.
🔐 Key 2021 Amendment (Cybersecurity Focus – Article 3.3 d/e/f):
Applies from August 1, 2025.
| Clause | Requirement | Applies To |
|---|---|---|
| 3.3(d) | Protection of communications over the Internet (e.g., encryption, secure protocols) | All connected devices |
| 3.3(e) | Protection of personal data and privacy | Devices processing user data |
| 3.3(f) | Protection against fraud (e.g., device spoofing, data manipulation) | Devices involved in payments, identity, or personal data |
🔗 Reference: EU RED Cybersecurity Regulation
📡 2. Impact on IoT Devices & Ecosystems
🔧 A. Technical & Design-Level Impacts
- Mandatory security-by-design: Devices must include encryption, secure boot, secure updates.
- Authentication & access control: Critical for cloud-connected and user-facing IoT.
- Software update mechanisms: OTA (Over-the-Air) updates must be secure and verifiable.
📝 B. Compliance and Documentation
- Technical documentation overhaul: Security features must be documented in CE conformity assessments.
- Notified Body involvement: In some cases, third-party assessment is needed (especially if harmonized standards are lacking).
- Updated CE marking: Must reflect compliance with new cybersecurity essential requirements.
🤝 C. Market Access
- Non-compliant products will be banned from EU markets after August 2025.
- Affects OEMs, importers, and distributors—not just manufacturers.
🚀 3. Strategic Implications for IoT Product Teams
| Function | Strategic Actions |
|---|---|
| Product Management | Incorporate RED compliance requirements into product roadmaps early. |
| Engineering/Architecture | Redesign for encryption, secure firmware, and secure communications. Leverage secure elements (e.g., TPM, HSM). |
| Compliance & Legal | Collaborate with Notified Bodies and update all documentation to include security mechanisms. |
| Marketing & Sales | Use compliance as a differentiator in B2B/B2G contracts; emphasize “EU-ready”, “secure-by-design” features. |
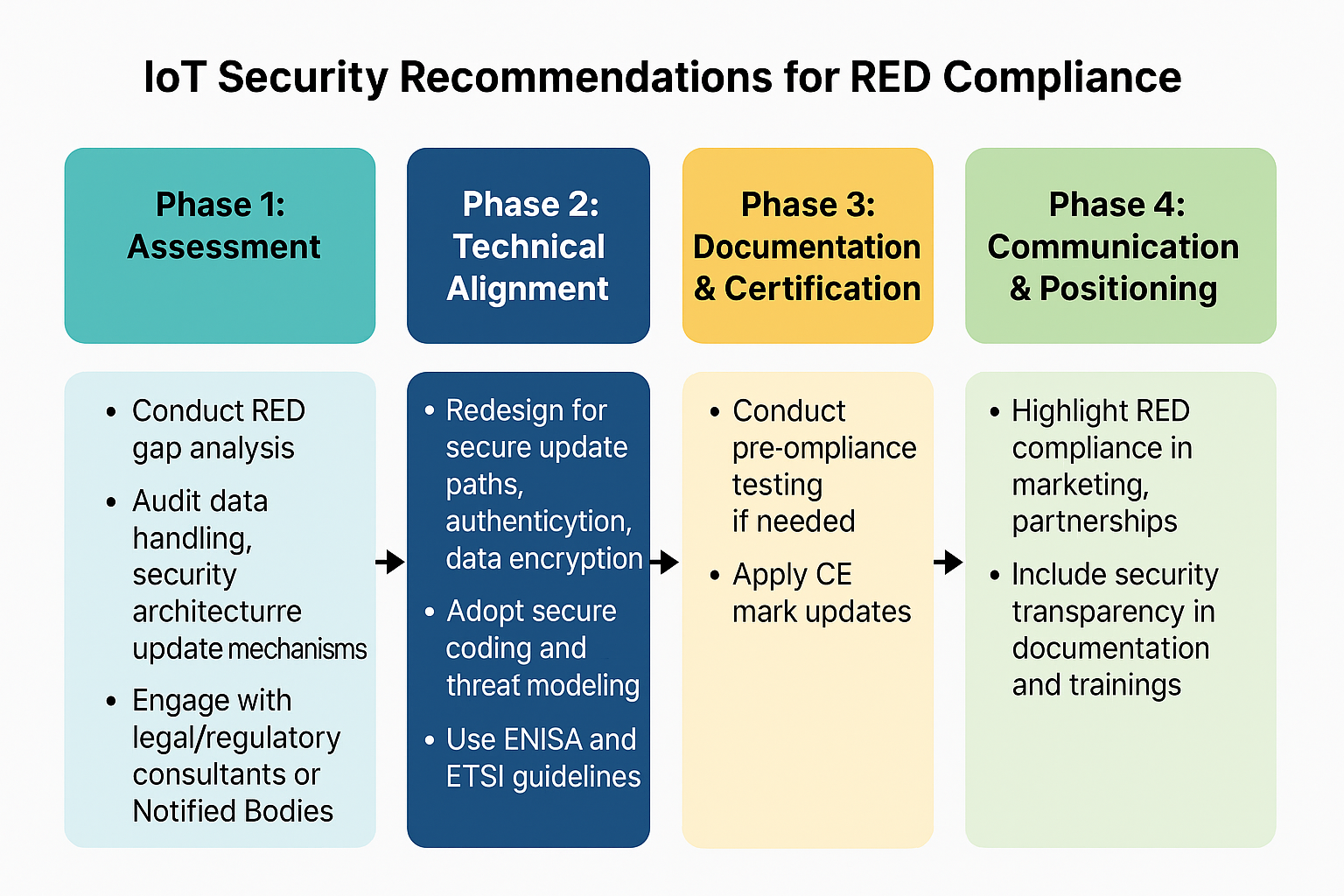
🛤️ 4. Way Forward: Roadmap for RED Compliance
🧭 Phase 1: Assessment
- Conduct a RED gap analysis across product lines.
- Audit data handling, security architecture, and update mechanisms.
- Engage with legal and regulatory consultants or EU Notified Bodies.
🔧 Phase 2: Technical Alignment
- Redesign firmware/software for secure update paths, authentication, and data encryption.
- Adopt secure coding practices and threat modeling (e.g., STRIDE, DFDs).
- Use ENISA and ETSI guidelines (e.g., ETSI EN 303 645 for consumer IoT).
🗂️ Phase 3: Documentation & Certification
- Prepare technical files, updated DoC (Declaration of Conformity).
- Conduct pre-compliance testing with labs if needed.
- Apply CE mark updates and ensure importer/distributor awareness.
📣 Phase 4: Communication & Positioning (Ongoing)
- Build market confidence by highlighting RED/CE compliance in B2B, tenders, and public sector deals.
- Include security transparency in user documentation and partner enablement kits.
EU Guidance RED Compliance Guidance – EU Commission