Generative AI in the Enterprise - Training/Inferencing on-premise
Despite the potential benefits of Generative AI in improving business processes, workflows, customer experience, and productivity, organizations may face several challenges in effectively utilizing this technology. Some of the challenges include:
- Data Privacy and Security
- Low Latency
- Regulatory Compliance
- Customization and Control
- Cost Considerations
- Offline Capability
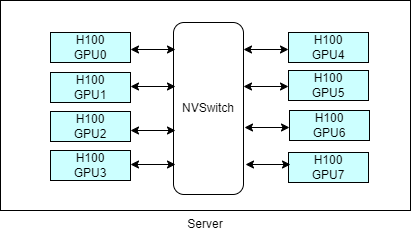
With the advancement of Hardware now Customer can use 8 GPU with 640 GB GPU(I H100 card with 80 GB GPU memory) memory on single server without facing any latency issue. Which is quite good for running couple of LLMs. But still there are scenario where we need More than 640 GB GPU memory for single LLM.
This can be solved by deploying both front-end and back-end infrastructure on-premise can provide organizations with greater control over their AI workloads, especially when dealing with large-scale models and datasets. Here’s a conceptual overview of how you can deploy front-end and back-end connectivity for scaling generative AI models across multiple compute nodes:
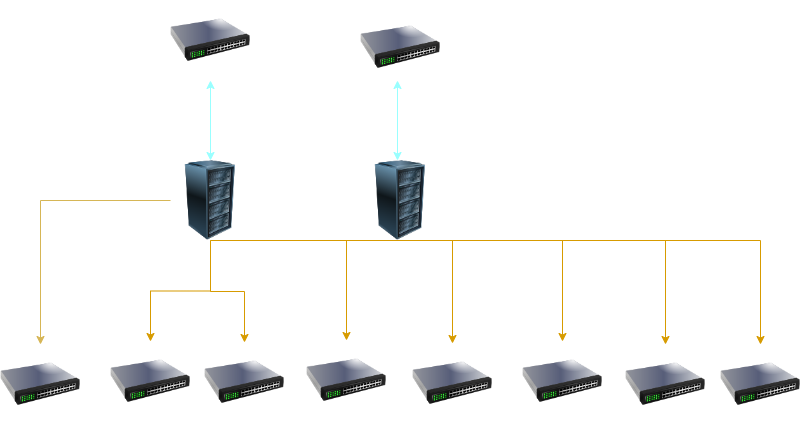
1. Front-End Connectivity:
a. Server Infrastructure:
- Utilize high-performance servers with advanced GPUs. For example, servers equipped with 8 GPUs and 640 GB GPU memory, such as the NVIDIA H100 GPUs or similar high-memory GPU cards.
b. Network Connectivity:
- Ensure high-speed interconnects between GPUs within a single server for efficient communication during model training or inferencing.
c. Scaling Compute Nodes:
- Deploy multiple servers with similar high-performance GPU configurations to scale computational power horizontally.
d. Load Balancing:
- Implement load balancing mechanisms to distribute inferencing tasks efficiently across multiple front-end compute nodes. This helps in optimal utilization of resources and prevents bottlenecks.
2. Backend Connectivity:
a. High-Speed Networking:
- Employ backend networks with speeds of 200/400 Gbps to facilitate fast communication between compute nodes.
b. Distributed Training:
- For large models or datasets that require more than the available GPU memory on a single node, implement distributed training across multiple nodes. Use high-speed networking to synchronize updates and gradients between nodes efficiently.
c. Model Parallelism:
- Divide large models into segments and distribute them across multiple GPUs or nodes. High-speed backend networks help in transmitting intermediate results quickly.
d. Data Parallelism:
- Distribute training data across nodes for parallel processing. Ensure that the backend network can handle the increased data transfer requirements.
e. Communication Optimization:
- Implement communication optimizations like gradient compression and asynchronous updates to minimize the communication overhead between nodes.
f. Scalability:
- Design the backend infrastructure to be scalable, allowing the addition of more compute nodes as needed. This ensures flexibility in handling growing workloads.
3. Deployment Workflow:
- Model Training:
- During the training phase, the distributed nature of the backend network enables training on larger datasets or more complex models that exceed the capacity of a single GPU or node.
- Inferencing:
- During inferencing, the front-end servers can efficiently process incoming requests, and the load balancer ensures a balanced distribution of tasks among available compute nodes.
- Scalability and Flexibility:
- The architecture is designed to be scalable both in terms of computational power (front-end) and memory capacity (backend), allowing the organization to adapt to changing requirements.
- Monitoring and Optimization:
- Implement monitoring systems to track the performance of both front-end and back-end components. Optimize configurations based on usage patterns and requirements.
- Security Considerations:
- Implement robust security measures for both front-end and back-end connectivity to safeguard data and models.
By combining high-performance GPUs with fast networking infrastructure, organizations can effectively deploy and scale generative AI models, addressing the challenges associated with large model sizes and demanding workloads. Continuous monitoring, optimization, and adherence to best practices ensure the efficiency and reliability of the deployed system.
Generative AI has the potential to bring about significant improvements in various aspects of business operations, leading to cost efficiencies and enhanced value for organizations